 Flagge "Flagge des Kanton Schaffhausen" bei fahnenversand.de kaufen.
Flagge "Flagge des Kanton Schaffhausen" bei fahnenversand.de kaufen.
 Flagge "Flagge des Kanton Schaffhausen" bei fahnenversand.de kaufen.
Flagge "Flagge des Kanton Schaffhausen" bei fahnenversand.de kaufen.
Last modified: 2025-03-15 by martin karner
Keywords: switzerland | schaffhausen | ram | sheep | german |
Links: FOTW homepage |
search |
disclaimer and copyright |
write us |
mirrors
Description of the Flag
Or, a ram sautant sable, crowned armed unguled and in his virility
gold, langued gules.
On a yellow field, a leaping black ram with golden horns, hooves,
penis, and crown, and a red tongue. This flag has a minor heraldic
error in that it combines actual gold with yellow, but there was a
conscious reason for this (see below).
T.F. Mills, 23 October 1997
Symbolism of the Flag
The ram is a prehistoric religious and martial symbol of virility
and power. Heraldry tends to emphasize virility by always depicting
male animals, and Swiss heraldry often specifies the colour of
genitals. Gold genitals may seem odd, but that was a papal decision
that even the Protestant Reformation did not change. The ram is
sometimes understood to be a play on the name of the city ("scaf" =
sheep), but this is incorrect, and the correct etymology is
"sca^fa-hausen", or "house of ships" (Schaffhausen is the
southernmost navigable point on the Rhine). The colours black and
yellow almost certainly are derived from the old imperial standard (black
eagle on a yellow field).
T.F. Mills, 23 October 1997
History of the Flag
Schaffhausen's development was closely tied to a Benedictine convent
founded in 1052. The city state became sovereign within the Holy
Roman Empire in 1218, and that is also the earliest documented
evidence of the flag. Schaffhausen fell under Austrian dominance in
1330 and did not regain its independence until 1415. It was
admitted to the Swiss confederation in 1501, two months after Basel.
The ram on the flag was originally unadorned, but Schaffhausen was
one of the recipients of a "Julius Banner" in 1512. The ram was
granted a golden crown, and its horns, hoofs and genitals were also
rendered in gold. The ram was originally "rampant" standing in the
classic one hoof position (rear left on the ground), but in the
1940s the ram was tilted forward to the "sautant" position with both
rear hoofs on the ground (i.e. landing from a jump). For a while
after the 13th century the city seal showed a ram jumping out of a
city gate, based on the erroneous etymology that Schaffhausen meant
"house of ;sheep".
T.F. Mills, 23 October 1997
– Early depictions of the heraldic animal, the ram, on Schaffhausen coins
from ca. 1160, 1280/90 and 1250 (see also coin on the commune page).
Location:
Museum zu Allerheiligen, Schaffhausen (source).
– Copy of the flag which was captured by the Swiss in 1386 at the
battle of Sempach (Schaffhausen was not yet part of the Swiss Confederation). It was designed in 1490 after the original, since the original captured flags hanging
in a church went rotten. Location: Historical Museum, Luzern (source).
– Stained glass plate (ca. 1550), ascribed to Felix Lindtmayer the Younger. CoA with imperial arms as a sign of
imperial immediacy, two warriors holding the banner and a halberd. Private property
(source).
– Stained glass plate (1560), asc. to Hieronymus Lang d.Ä.,
with pyramid of arms above the arms of Paradies monastery, and two lions. Location: Paradies,
Eisenbibliothek (former monastery) (source).
– Dragoon standard (1713, 140x125 cm). On black cloth a yellow
medallion framed by a laurel wreath, showing a black ram with golden crown, virility and hooves. On the upper
edge with golden letters Schaffhausen's motto "DEUS SPES NOSTRA EST" (God is our hope), on the lower
edge the year "1713". Yellow-black-green fringes on three sides (b/w photo, source: [b7b42]).
Colour Flag
![[Colour Flag SH]](../images/c/ch-sh_56.gif) image
by Ole Andersen
image
by Ole Andersen
Simple rectangular cantonal flag, as shown in Kannik (1956)
[So-called colour flag (Farbenfahne in German)].
Ole Andersen, 4 August 2002
See also: STATE COLOURS in Dictionary of Vexillology
Flaggen, Knatterfahnen and Livery Colours |
![[Knatterfahnen]](../images/c/ch-sh_kf.gif)
|
Flaggen are vertically hoisted from a crossbar in the manner of gonfanon, in ratio of about 2:9, with a swallowtail that indents about 2 units. The chief, or hoist (square part) usually incorporates the design from the coat of arms – not from the flag. The fly part is always divided lengthwise, usually in a bicolour, triband or tricolour pattern (except Schwyz which is monocolour, and Glarus which has four stripes of unequal width). The colours chosen for the fly end are usually the main colours of the coat of arms, but the choice is not always straight forward.
Knatterfahnen are similar to Flaggen, but hoisted from the long side and have no swallow tail. They normally show the national, cantonal or communal flag in their chiefs.
Željko Heimer, 16 July 2000
Why are the livery colours unexplainable from the coat of arms?
António Martins, 17 April 2001
The livery colours of Schaffhausen canton are not taken from the coat of arms. Originally, the pennon which preceded the banner was green. The laces of green colour (alone or accompanied by another one) attached to the majority of the official acts established between 1253 and 1321 attest it. An invoice from 1444 takes into account the purchase of green and black material. The black attested here as the second colour of the city can derive from the ram appearing on the banner. Since that date, all documents prove that green and black were the official colours until the end of the Ancien Regime. This fact confirms that blazons, banners and cantonal colours are not always identical and, for this reason, one need to follow their historical evolution.
Pascal Gross, 6 April 2001
Kannik (1956) mentions that the colours go back to round 1500
(Znamierowski, 2000, says 15th century), and notes that the livery colours are or and sable. Kannik also shows the canton flag as green over black.
Ole Andersen, 18 April 2001
See also: HANGING FLAG, VERTICALLY HOISTED FLAG, LIVERY COLOURS in Dictionary of Vexillology

 images located by Martin Karner
images located by Martin KarnerAt the beginning of the 20th century, flamed flags were still in use, with the white cross replaced by
a (baroque) shield in the centre of the flag. These decorative flags had been used until WWII and then
somewhat forgotten in preference of the current cantonal flags. [Today they are being
produced again, see right image]
Pascal Gross, 30 June 2002
See also: • National flag and other cantonal flags with "Early 20th century flag design"
• Modern flamed flags
• FLAMMES in Dictionary of Vexillology
logo.jpg) image located by Martin Karner (8 May 2024)
image located by Martin Karner (8 May 2024)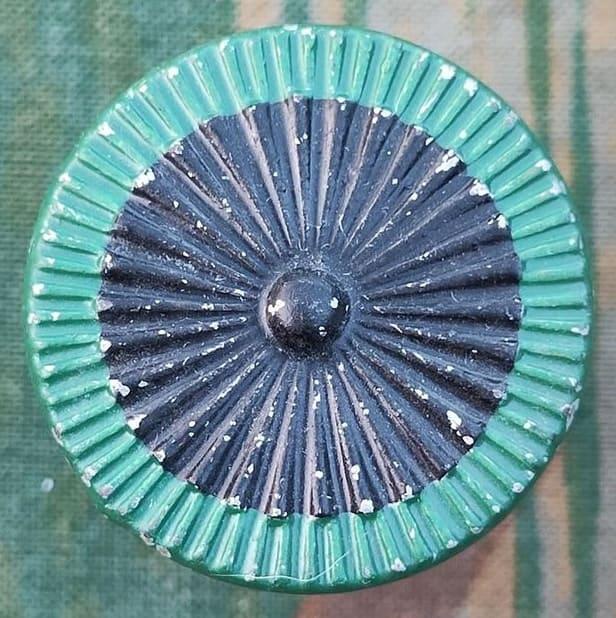 image located by Martin Karner
image located by Martin KarnerCockade for the cantonal troops' headgear (regulation from 1898, size: ca. 35 mm, reverse side).
Martin Karner, 14 March 2025
See also: Cockades (Swiss Army)







